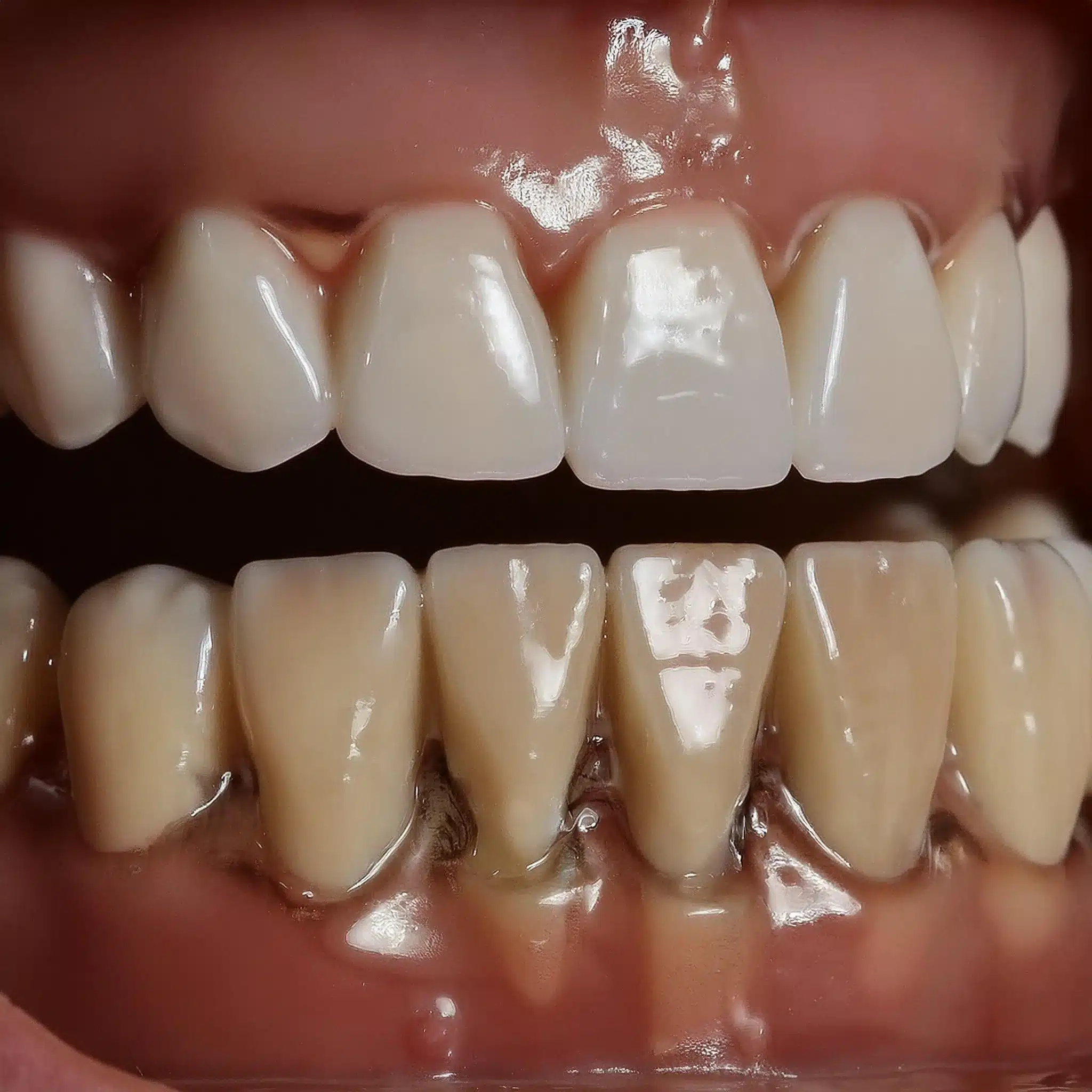
Tissue grafting is a must-have for anyone looking to restore their smile and confidence, but what is tissue grafting and how can it help me with my dental issues?
If you have soft tissue deficiencies or esthetic problems around your teeth or implants, such as gum recession, understanding tissue grafting is the key to getting the smile you want.
What is Tissue Grafting?
Tissue grafting is a dental procedure to repair and augment soft tissue deficiencies around teeth and implants to achieve esthetic and functional results. It involves moving healthy tissue from one part of the mouth to another with up to a 95% success rate in achieving desired esthetic and functional results.
Types of Tissue Grafts
Connective Tissue Grafts
A connective tissue graft is used to address gingival recession and improve the esthetics of teeth. This procedure involves harvesting tissue from the palate and placing it over the exposed root surfaces.
Connective tissue grafts have been proven to be successful with high patient satisfaction and root coverage.
In one study, a minimally invasive approach using connective tissue grafts resulted in 100% root coverage and 95% patient satisfaction due to esthetics and reduced sensitivity (1)
Free Gingival Grafts for Gum Tissue
Free gingival grafts are used to add thickness to the gum tissue and prevent further recession.
This involves taking a thin layer of tissue from the palate and attaching it to the gum area that needs augmentation.
While this method works to add thickness, it’s less esthetic than connective tissue grafts.
However, it’s a good option for patients with thin gingival biotypes or those who need extra tissue support.
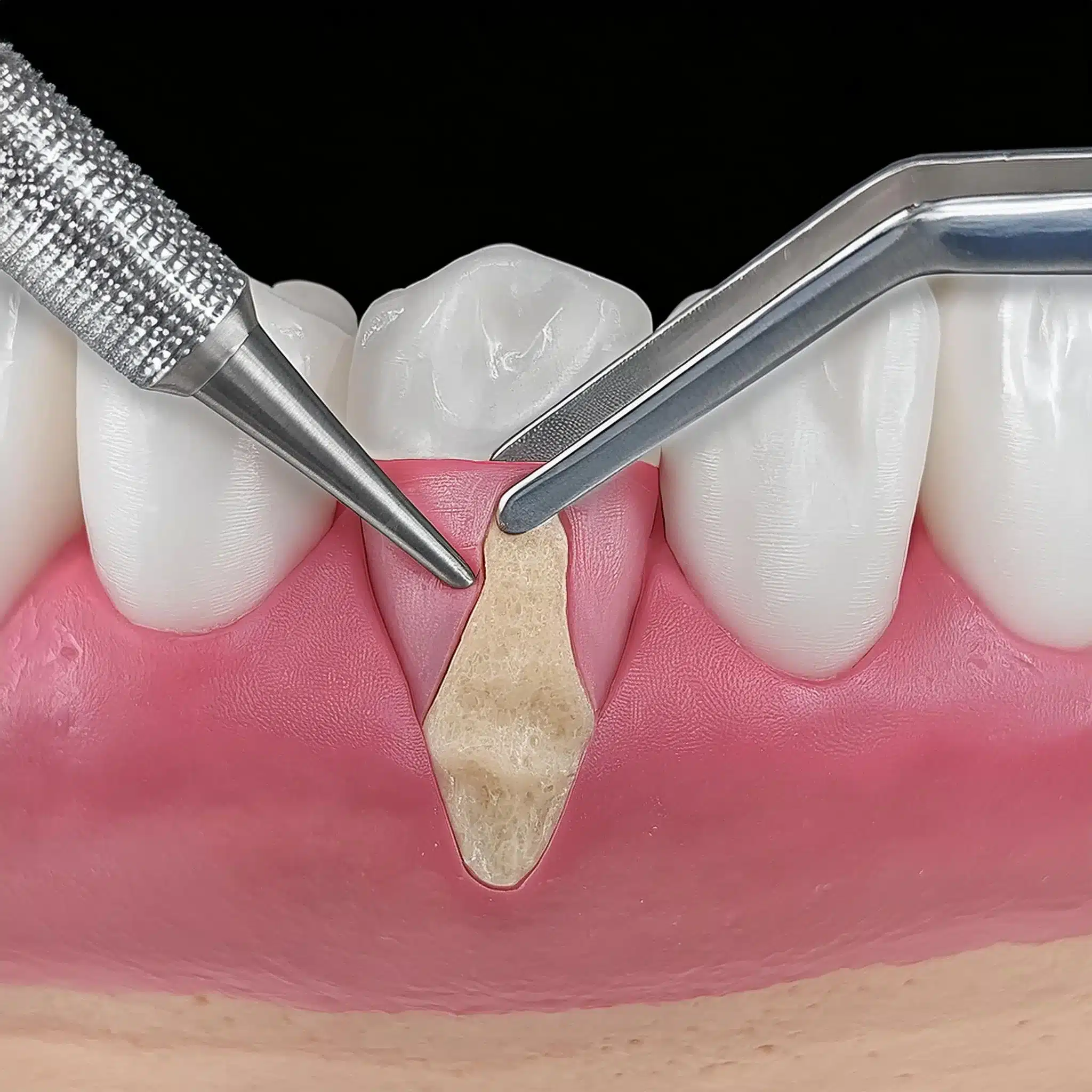
Subepithelial Grafts
Subepithelial grafts are a versatile option for both esthetic and functional results.
This involves placing the graft beneath the existing gum tissue to achieve a natural look and add support to the gum line.
Subepithelial grafts are good for areas that need both volume and coverage, a balanced solution for complex cases.
Using subepithelial grafts with guided bone regeneration showed significant improvement in bone stability and esthetic results, with 95% of cases maintaining bone level stability (2).
Indications for Tissue Grafting
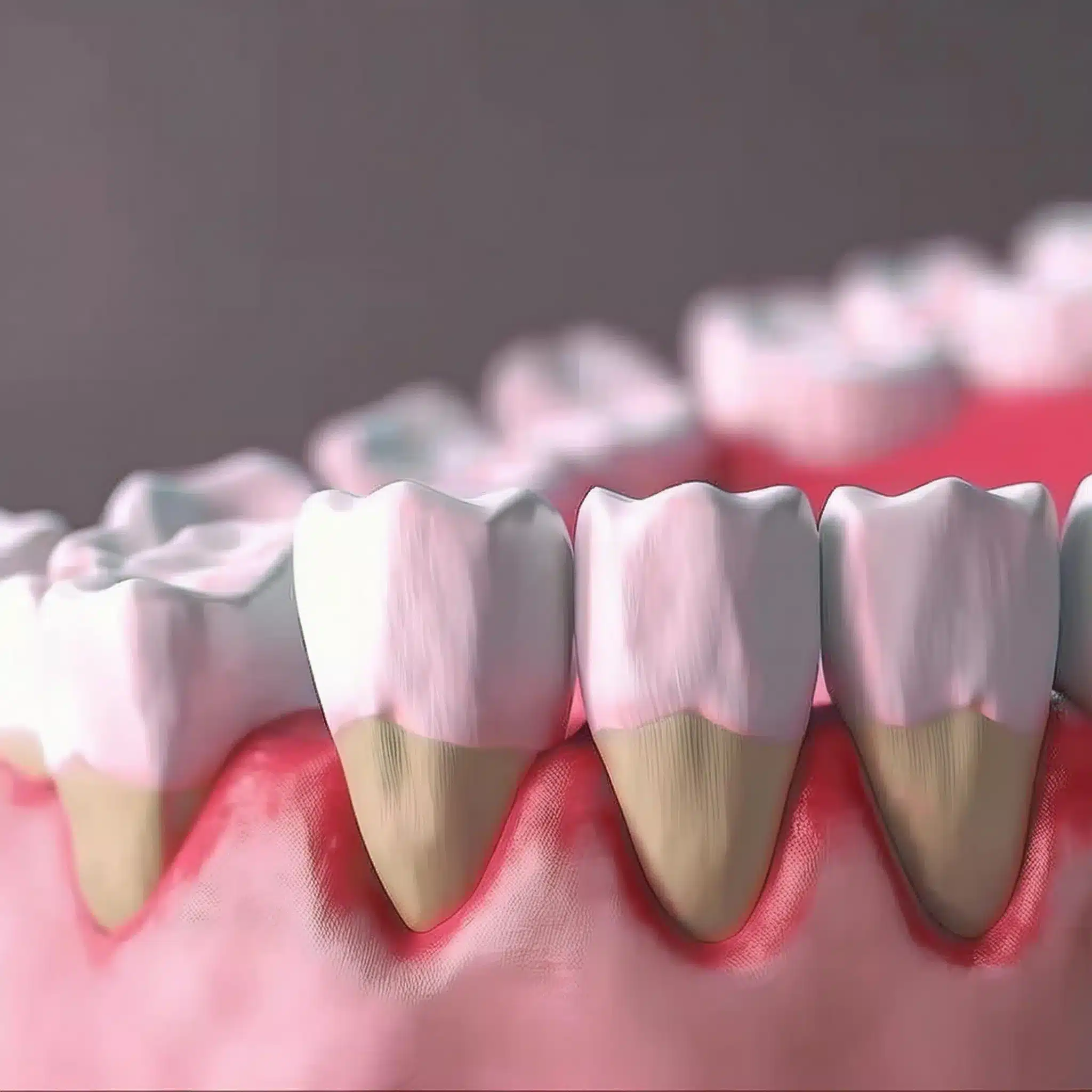
Gum Recession
Gingival recession is an indication for tissue grafting as it can cause esthetic and functional problems.
Tissue grafting can cover exposed tooth root surfaces, improve the appearance of the teeth, and reduce sensitivity.
A study on autogenous soft tissue grafting for periodontal and peri-implant defects showed the effectiveness of this procedure in managing gingival recession with up to 90% success rate in achieving desired esthetic and functional results (4).
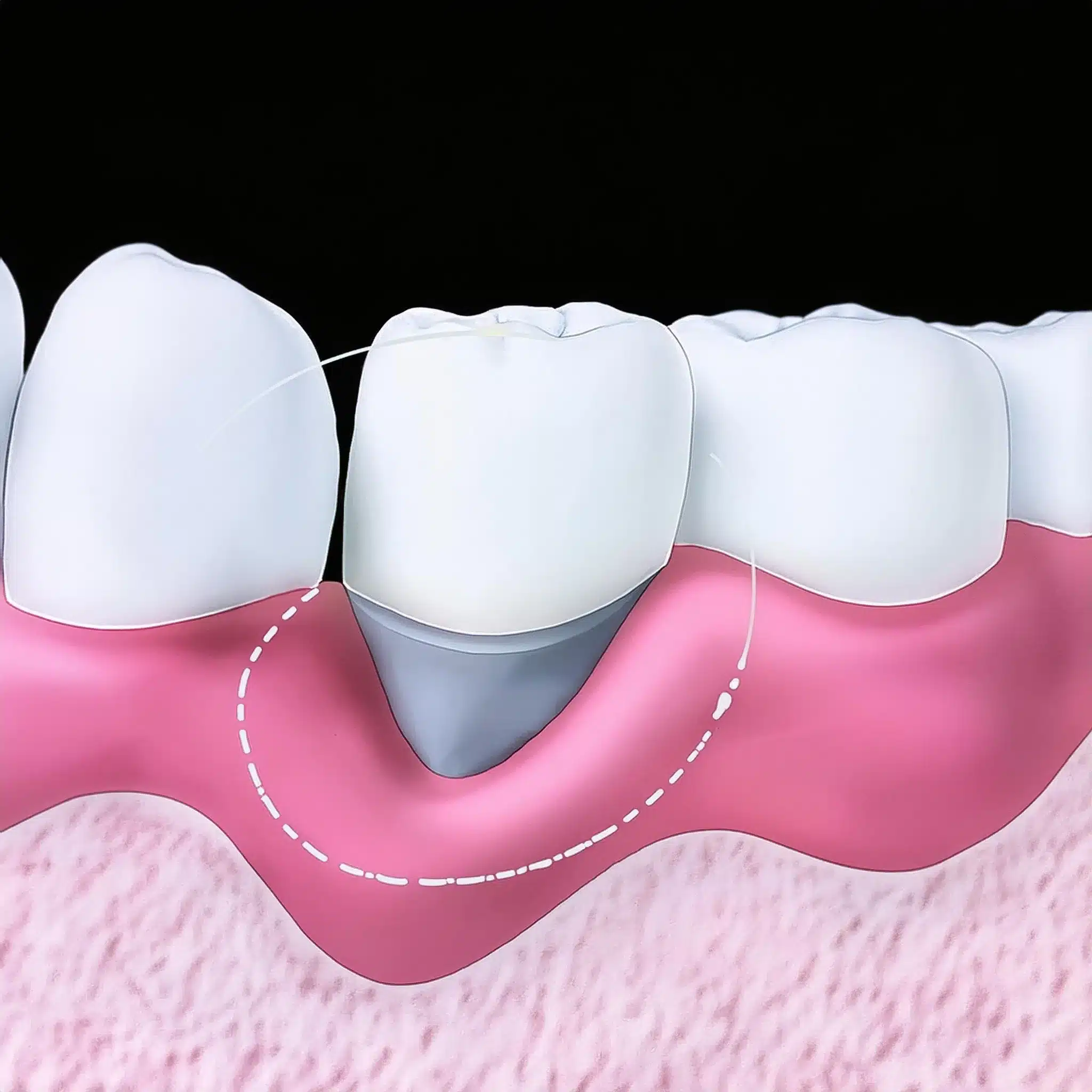
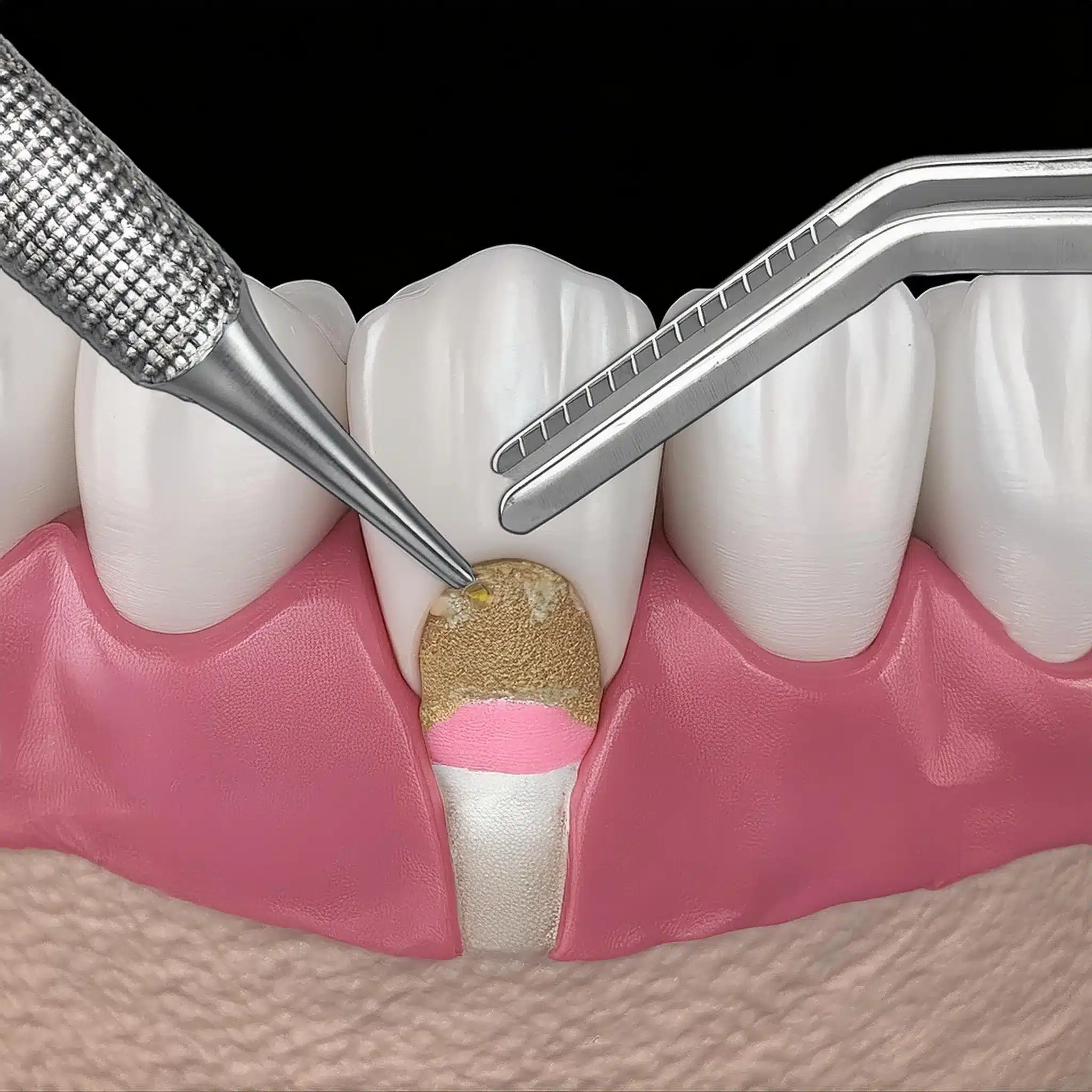
Root Coverage Techniques for Exposed Tooth Root
Root coverage techniques are the key in tissue grafting for gingival recession.
These involve placing a graft over the exposed root surface to achieve a natural look and functional stability.
Subepithelial connective tissue grafts have been shown to be effective in root coverage, with 95% root coverage in treated areas (3).
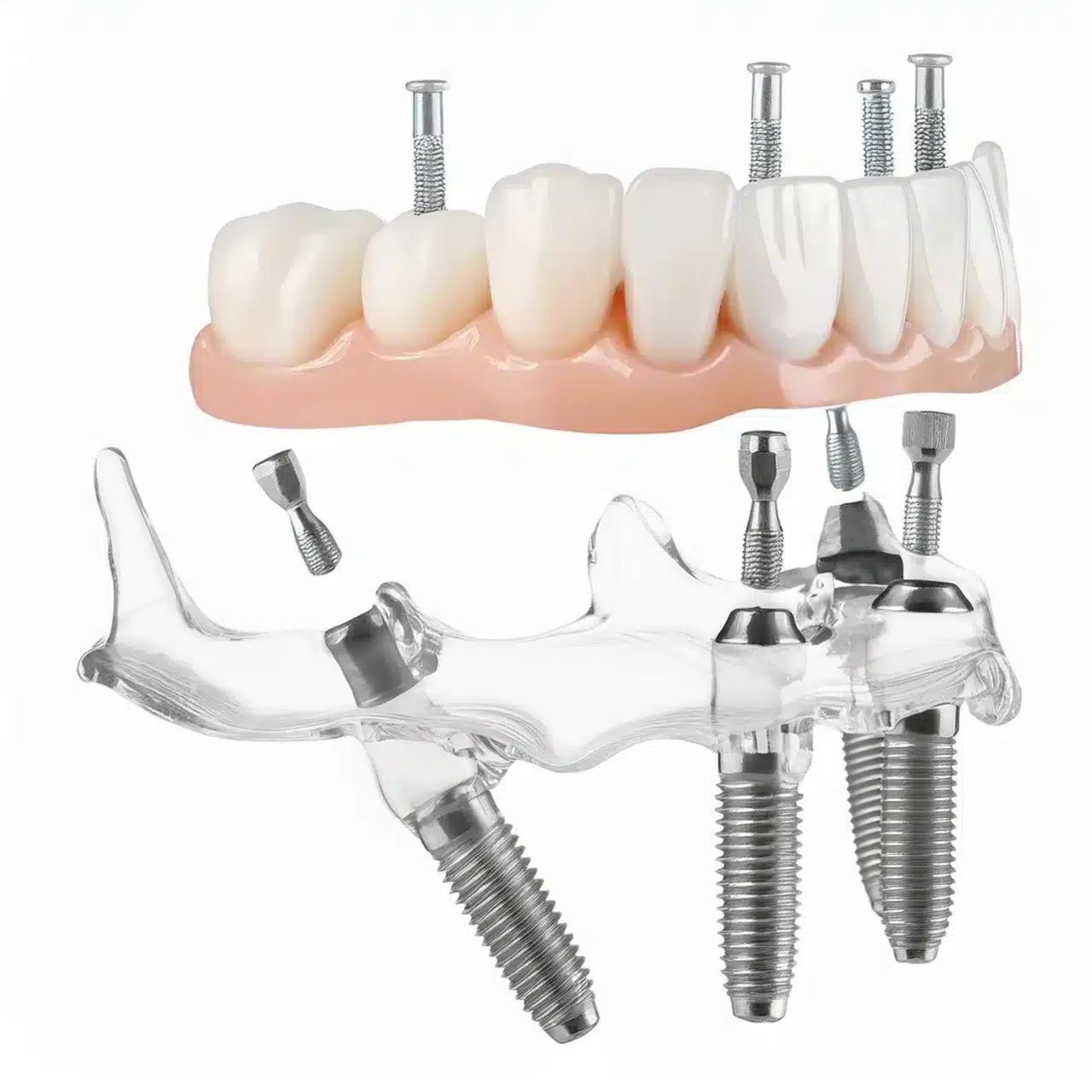
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation
Alveolar ridge augmentation is another indication for tissue grafting, especially in cases where dental implants with bone loss are planned.
This procedure, often performed alongside a sinus lift in the upper jaw, can enhance the volume and shape of the alveolar ridge, improving the esthetic and functional outcomes of implant placement
Tissue grafting can add volume and shape to the alveolar ridge and improve the esthetic and functional results of implant placement.
A retrospective controlled study on immediate implantation and provisionalization with guided bone regeneration showed 95% bone level stability, which is critical for long-term success of dental implants (2).
Surgical Techniques in Soft Tissue Grafting
Harvesting Methods
Harvesting methods are critical in tissue grafting procedures.
The harvesting technique can affect the quality and quantity of the graft and the donor site morbidity.
A study on autogenous bone grafting showed the importance of meticulous harvesting techniques to minimize complications and get optimal graft (3).

Suturing Techniques
Suturing techniques are key to securing the graft in place and healing.
Using the right suturing technique can prevent complications such as graft displacement or failure.
A study on skin grafting emphasized the importance of proper suturing technique to get graft survival and minimize complications (2).
Post-operative Care and Recovery
Postoperative care and recovery are important parts of tissue grafting procedures.
Proper wound care and follow-up can prevent complications and get optimal healing.
A study on mandibular ramus block grafting showed minimal postoperative complications when proper care and follow-up were given (3).
Expected Outcomes and Risks
Success Rates of Tissue Grafts
Tissue grafting has shown a high success rate in achieving desired esthetic and functional results.
A long-term study showed 83% of sites that received free gingival grafts maintained reduction of recession up to 35 years (2).
This proves the durability and effectiveness of tissue grafting in managing gingival recession.
Complications and Management
Tissue grafting is generally a safe procedure, but complications can occur.
Common complications are bleeding, swelling, and pain at the donor and recipient sites.
In rare cases, infection or graft failure can occur.
A study on subepithelial connective tissue grafts showed a 10-15% complication rate; thus, proper postoperative care and follow-up are important.
Complication management is key to getting optimal results and patient satisfaction.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Çelës-Takeaways
Tissue grafting is a versatile procedure for soft tissue deficiencies and aesthetic results.
Different types of tissue grafts (connective tissue, free gingival, subepithelial) can be used depending on the patient’s needs.
Up to 95% success rate in achieving aesthetic and functional results.
konkluzioni
Tissue grafting is a must for those who want to get back their smile and confidence.
By knowing the types of tissue grafts, indications for grafting, surgical techniques, and expected outcomes, patients can make informed decisions for their dental care.
With a high success rate and minimal complications, tissue grafting is a reliable solution for soft tissue deficiencies and aesthetic results.
Pyetjet e shpeshta
Referencat
Howe MS, Keys W, Richards D. Long-term (10-year) dental implant survival: A systematic review and sensitivity meta-analysis. J Dent. 2019;91:103-113.
Neni: Long-term (10-year) dental implant survival: A systematic review and sensitivity meta-analysisSu Z, Chen Y, Wang M, Mo A. Evaluation of Immediate Implantation and Provisionalization Combined with Guided Bone Regeneration by a Flap Approach in the Maxillary Esthetic Zone: A Retrospective Controlled Study. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(14):3874.
Neni: Evaluation of Immediate Implantation and Provisionalization Combined with Guided Bone Regeneration by a Flap Approach in the Maxillary Esthetic Zone: A Retrospective Controlled StudyHamid N, et al. Soft Tissue Grafting Procedures before Restorations in the Esthetic Zone: A Minimally Invasive Interdisciplinary Case Report. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2023;35(4):102-110.
Neni: Soft Tissue Grafting Procedures before Restorations in the Esthetic Zone: A Minimally Invasive Interdisciplinary Case ReportZucchelli G, Tavelli L, Stefanini M, et al. Classification of facial peri-implant soft tissue dehiscence/deficiencies at single implant sites in the esthetic zone. J Periodontol. 2019;90(10):1116-1124.
Neni: Classification of facial peri-implant soft tissue dehiscence/deficiencies at single implant sites in the esthetic zone