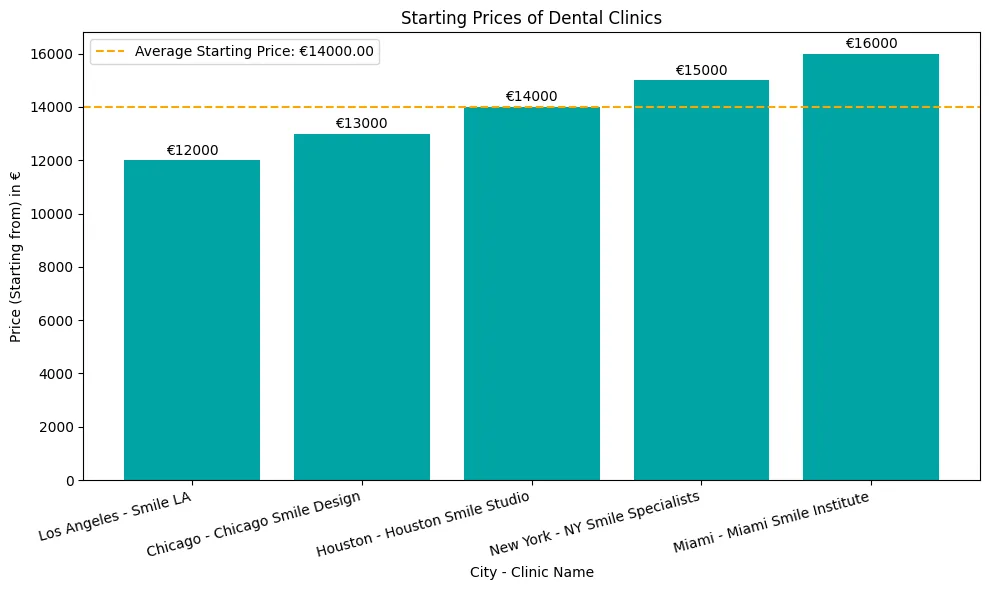
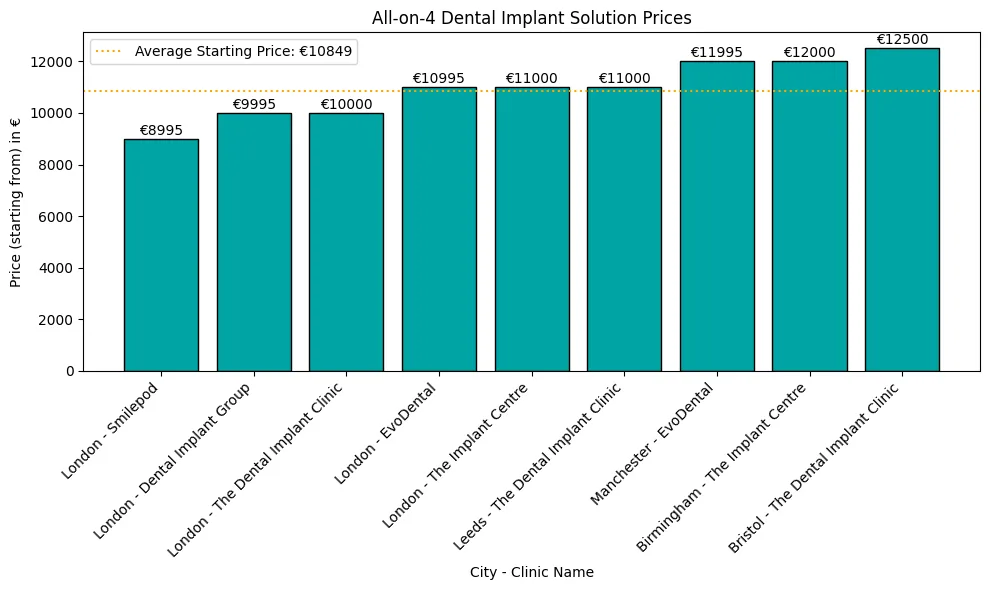
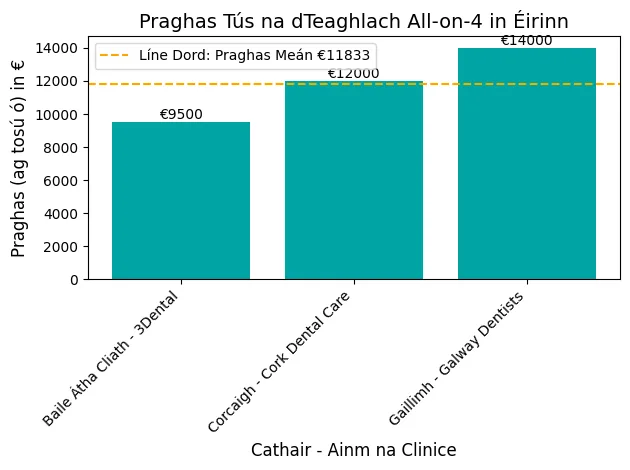
Loose implants can be a real pain, and many wonder what causes this and how to fix it.
If your dental implant feels loose, it can be concerning, but understanding the causes and solutions is key to your oral health and peace of mind.
If you’re experiencing discomfort or uncertainty about your implant, understanding the causes and solutions is key to your oral health and peace of mind.
Dental implant risks and complications
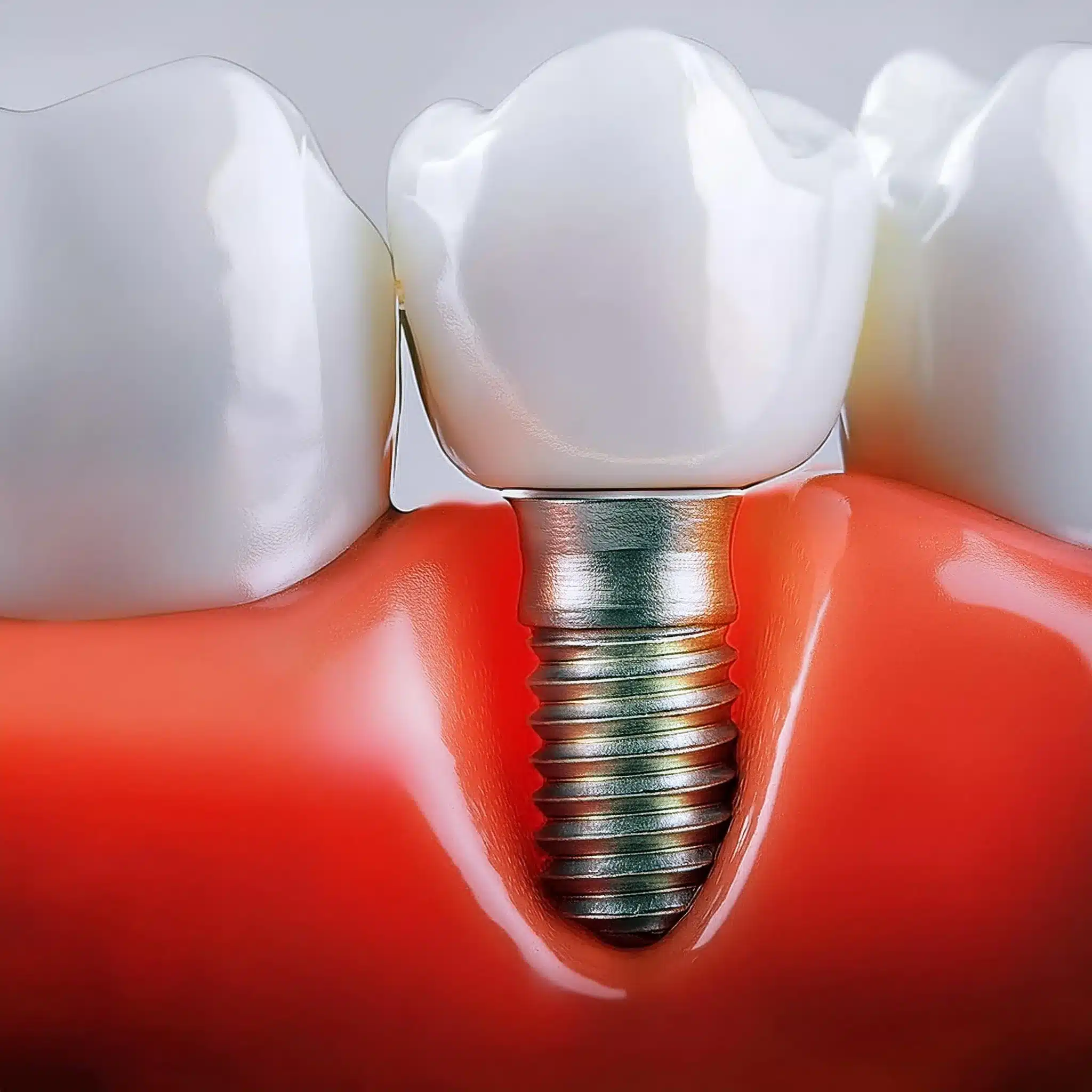
Loose dental implants can be caused by inadequate bone density, wrong placement or not enough healing time.According to recent studies, immediate-delayed implants show higher patient satisfaction and better esthetic results than delayed implants. Causes of Loose Implants:
• Inadequate bone density
• Wrong placement
• Not enough healing time
• Poor oral hygiene and care
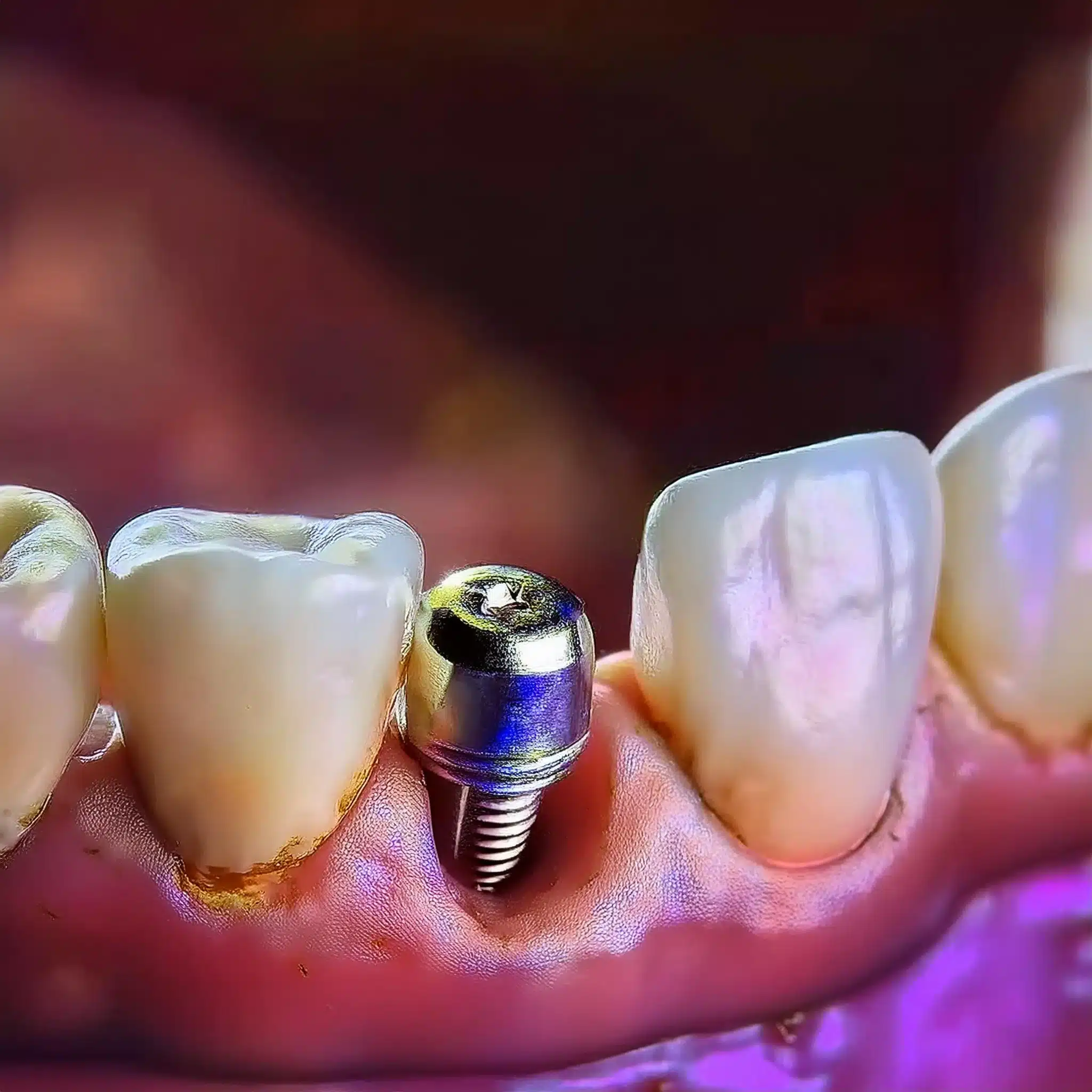
Symptoms of Loose Implants
Loose implants can be scary, but recognising the symptoms early makes all the difference.
Understanding these risks and complications symptoms is key to oral health and implant longevity.
Signs of Implant Loosening
Loose implants show specific symptoms that should not be ignored.
These are:
Mobility: Any movement of the implant when you touch it or during chewing is a clear sign of loosening.
Discomfort or Pain: Pain around the implant site that persists or worsens over time is a problem.
Swelling or Inflammation: Swelling or redness around the implant area is an indication of something is wrong.
Changes in Bite: Shift in how your teeth align when you bite could mean the implant is not secure.
Early detection is key.
Studies show that recognising these signs early prevents further complications and better treatment(3).
Why Early Detection Matters
Detecting a loose implant early makes a big difference in treatment success.
Here’s why early detection is important:
Prevents Further Damage: Catch it early and prevent further damage to surrounding bone and tissues.
More Treatment Options: Early intervention gives you more treatment options, potentially avoiding more invasive procedures.
Better Success Rates: Timely treatment can improve chances of saving the implant, as clinical studies show better results with early intervention (5).
How are Loose Implants Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a loose dental implant is key to treatment and preventing further complications.
A thorough examination by a dentist is essential to getting an accurate diagnosis.
Examination Techniques
Several techniques are used to diagnose loose dental implants:
Clinical Examination: A full intraoral and extraoral examination is done to assess the implant’s stability and look for symptoms like pain or swelling.
Radiographic Assessment: Periapical radiographs are used to detect peri-implant radiolucency, which means bone loss around the implant. But radiographic findings alone may not always correlate with implant mobility (6).
Mobility Testing: The implant is gently moved to test its stability. Increased mobility is a clear sign of loosening and needs immediate attention (6).
Occlusal Examination: Occlusal examination helps to identify non-axial forces that may contribute to implant loosening. This includes checking for high occlusal loads or misalignment (4).
| Technique | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Examination | Intraoral and extraoral assessment to check for stability and symptoms like pain or swelling. | To identify physical signs of implant loosening. |
| Radiographic Assessment | Use of periapical radiographs to detect bone loss around the implant. | To visualize bone integrity and implant positioning. |
| Mobility Testing | Gentle manipulation of the implant to assess its stability. | To confirm the presence of implant movement. |
| Occlusal Examination | Evaluation of occlusion to identify non-axial forces affecting the implant. | To detect occlusal issues contributing to loosening. |
Treatment for Loose Implants and Dental Implant Failure
Loose implants need to be treated comprehensively, considering both surgical and non-surgical options.
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the problem and the underlying cause.
Professional dental implants repair may involve surgical procedures when necessary to fix or replace the implant, potentially including bone grafting to enhance the implant site or adjusting the implant position for better stability
Surgical and Non-surgical Interventions in Dental Implant Surgery
Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgery may be needed to repair or replace the implant. This could be bone grafting to the implant site or adjusting the implant position for better stability (6).
Non-surgical Interventions: For less severe cases, non-surgical methods like tightening the abutment screw or using dental cement to secure the implant temporarily may be enough (3).
Immediate Action: If the implant is painful, immediate removal of all components may be necessary to prevent further complications(6).
Professional Consultation: Consult a dentist to determine the best course of action. They can assess the situation and recommend the right treatment (5).
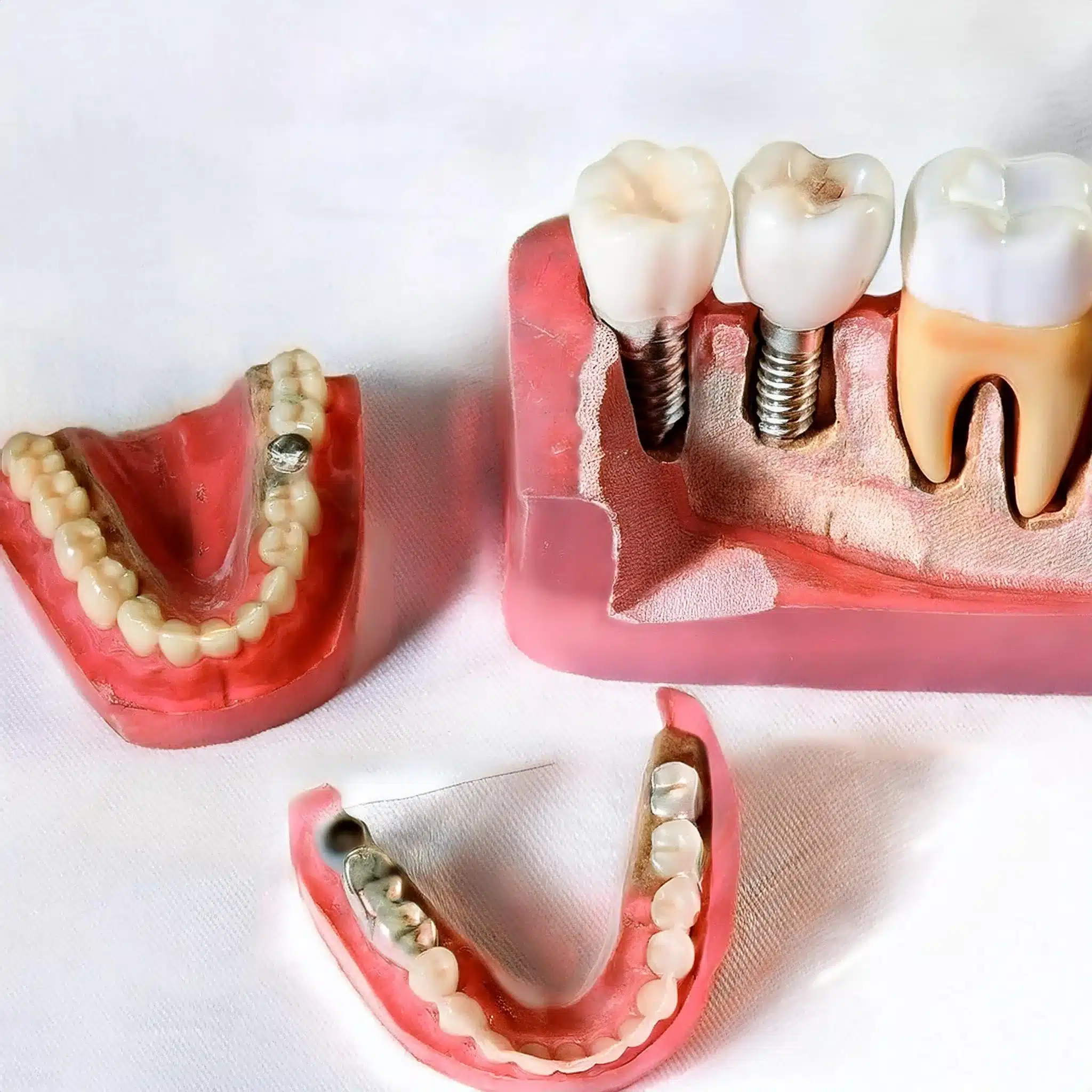
Dental implant repair
Dental implant repair is key to oral health and implant longevity.
Effective measures can reduce complications.
Oral Hygiene and Care
Daily Cleaning: Brush twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and non-abrasive toothpaste to remove plaque and food particles (7).
Flossing: Use unwaxed tape or implant-specific floss to clean around the implant and under the gum line gently to reduce peri-implantitis (6).
Mouthwash: Use alcohol-free mouthwashes to avoid dryness and irritation in the mouth that can harm the soft tissues around the implant (1).
Regular Check-ups: Regular visits to your dentist are essential to monitor the implant and the surrounding tissues (2).
Professional Cleaning: Dental hygienists use special tools designed for cleaning around implants to remove plaque and tartar buildup without damaging the implant surface (3).
Dietary: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains promotes overall health, including oral health, and reduces plaque accumulation (4).
Lifestyle Habits: Avoid habits that can physically damage your implants, like biting on hard objects or using your teeth as tools, and consider quitting smoking to enhance implant success (5).

Conclusion & Key-Takeaways
Key-Takeaways
Early Detection: Recognize the signs of a loose implant early to treat effectively and prevent further complications.
Customized Treatment Plan: A thorough assessment and customised treatment are key to treating loose implants.
Preventive Measures: Regular check-ups, good oral hygiene, and a healthy diet are essential for implant integrity.
Conclusion:
In summary, treating a loose implant requires a holistic approach, from understanding the causes and symptoms to choosing the right treatment.
Follow preventive measures and seek professional help early to ensure implant longevity.
FAQ
References
(1) Esposito M, et al. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: dental implants in fresh extraction sockets. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;(3):CD005968.
Article: Interventions for replacing missing teeth: dental implants in fresh extraction sockets
(2) Panchal M, et al. Dental implants: A review of types, design analysis, materials, additive manufacturing methods, and future scope. Procedia CIRP. 2022;105:2142-2148.
(3) Guillaume B. Dental implants: A review. Morphologie. 2016;100(329):189-198.
Article: Dental implants: A review
(4) Misch CE, et al. Dental implants: a review. J Oral Implantol. 1992;18(3):239-246.
Article: Dental implants: a review
(5) Albrektsson T, et al. Dental Implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2017;19(5):857-872.
Article: Dental Implants
(6) Branemark PI, et al. Dental Implants: The Last 100 Years. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75(10):2065-2075.
Article: Dental Implants: The Last 100 Years
(7) Salem Dental. Loose Dental Implants: Understanding the Causes and Solutions. Salem Dental. 2023.
Article: Loose Dental Implant: Understanding the Causes and Solutions