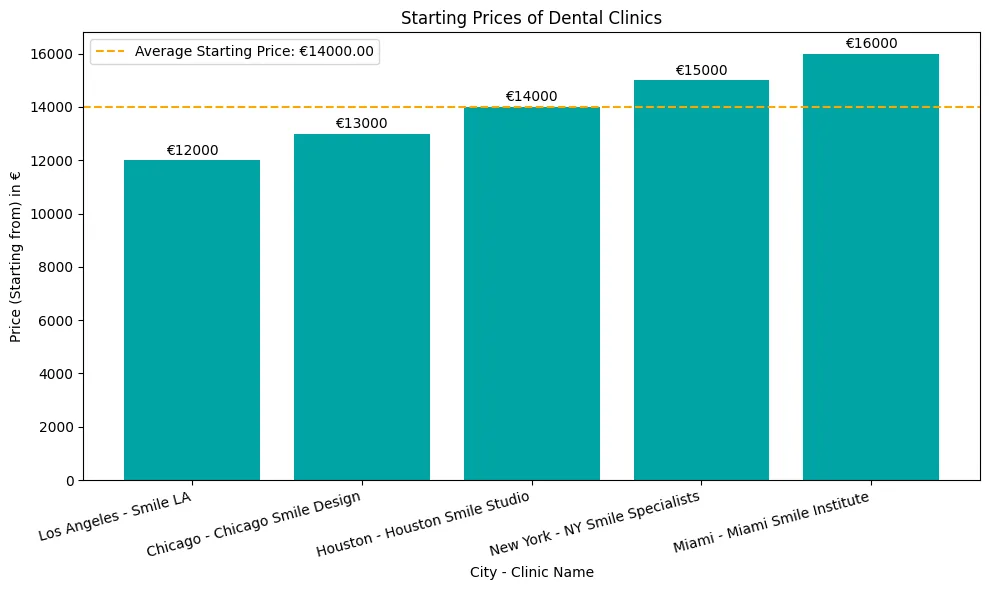
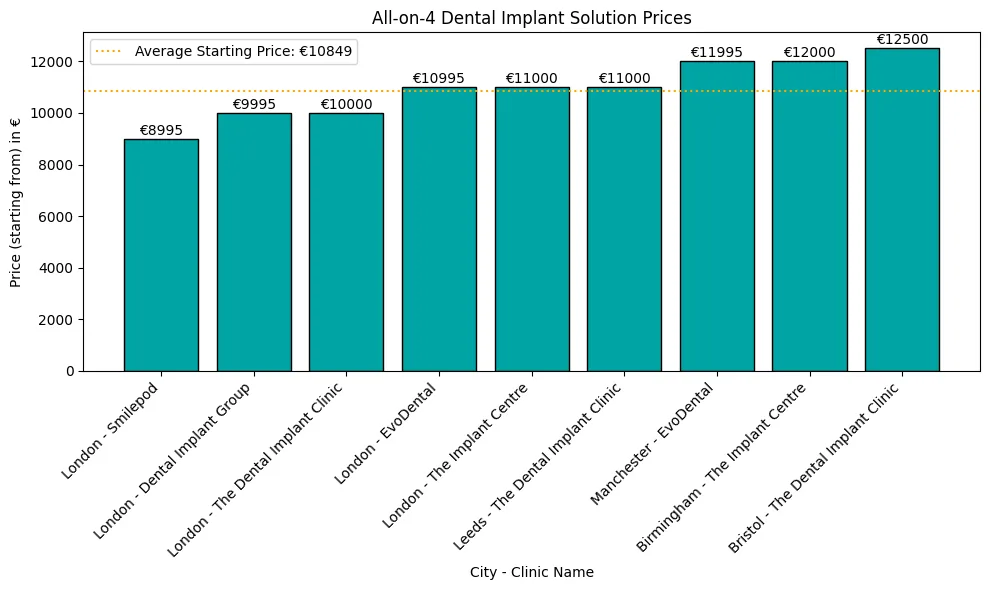
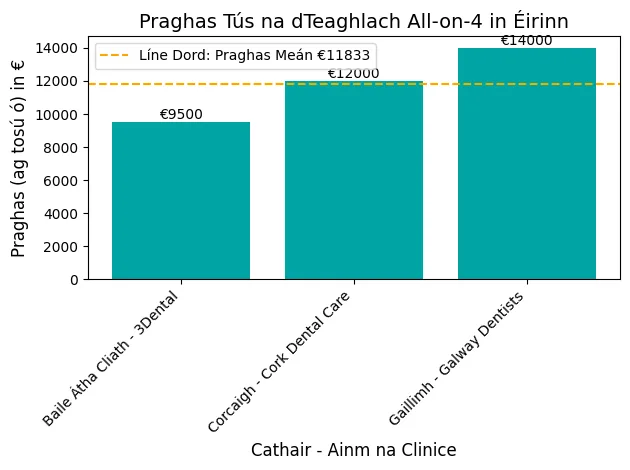
Implants dentaires pour les personnes âgées sont très importantes pour de nombreuses personnes âgées qui souhaitent retrouver leur santé bucco-dentaire et leur confiance en elles.
Si vous êtes une personne âgée et que vous envisagez de vous faire poser des implants, vous vous demandez probablement s'ils sont efficaces, s'ils durent longtemps et s'ils vous conviennent.
Qu'est-ce que les implants dentaires pour les personnes âgées ?
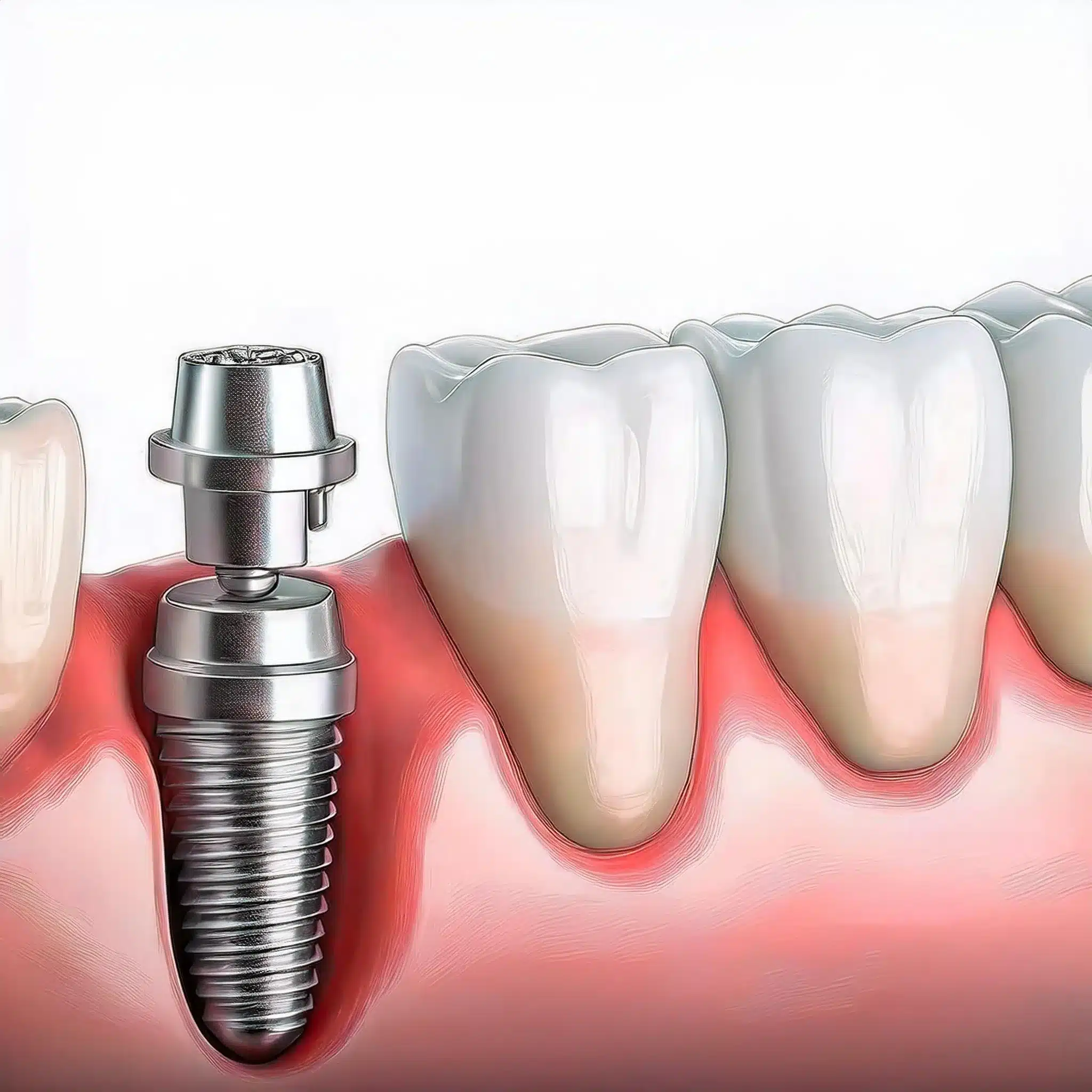
Les implants dentaires pour les personnes âgées sont une solution fiable pour les dents manquantes, la santé bucco-dentaire et le bien-être général. Ils sont fabriqués à partir de matériaux biocompatibles comme le titane et ont un taux de réussite de 95% sur 10 ans, ce qui en fait une option rentable et durable. Les personnes âgées doivent tenir compte de la densité osseuse et de leur état de santé général avant de procéder à la pose d'un implant.

Avantages des implants dentaires pour les personnes âgées
Santé bucco-dentaire
Les implants dentaires constituent une solution stable et durable pour les dents manquantes, ce qui peut grandement améliorer la santé bucco-dentaire des personnes âgées.
En remplaçant les dents perdues, les implants aident à maintenir la densité de l'os de la mâchoire et à prévenir la perte osseuse qui se produit après l'extraction d'une dent.
Cette préservation de la structure osseuse soutient les dents restantes ainsi que la structure et l'apparence du visage.
L'utilisation de matériaux biocompatibles comme le titane garantit un taux élevé de réussite de l'ostéointégration ; les études montrent 90-95% (1)(2).
Cette intégration à l'os donne une sensation et une fonction naturelles, comme les dents naturelles, ce qui permet aux personnes âgées de suivre un régime alimentaire varié sans restrictions.

Qualité de vie
Les implants dentaires peuvent grandement améliorer la qualité de vie des personnes âgées en leur permettant de manger et de parler correctement.
Les dents manquantes peuvent entraîner des difficultés de prononciation et de mastication, ce qui affecte l'alimentation et les interactions sociales.
Les implants sont une solution permanente qui offre la même sensation et le même fonctionnement que les dents naturelles. Ils renforcent la confiance en soi et permettent aux personnes âgées de participer davantage aux activités sociales.
On ne saurait trop insister sur les avantages psychologiques d'une dentition complète, qui contribue à une image positive de soi et à un bien-être général.
Rentabilité à long terme
Si le coût initial des implants dentaires peut être plus élevé que celui d'autres options de remplacement des dents, ils sont rentables à long terme.
Contrairement aux prothèses dentaires ou aux bridges, qui peuvent nécessiter des ajustements ou des remplacements fréquents, les implants sont conçus pour durer toute une vie s'ils sont correctement entretenus.
Cette durabilité se traduit par une réduction des travaux dentaires et des coûts à long terme.
En outre, les implants permettent d'éviter d'autres problèmes dentaires liés aux dents manquantes, tels que le déplacement des dents adjacentes ou des problèmes d'occlusion, ce qui peut entraîner des coûts supplémentaires (3).
En investissant dans des implants, les personnes âgées peuvent bénéficier d'une solution stable et durable pour leur santé bucco-dentaire et leur bien-être financier.
Qui peut recevoir des implants dentaires ? En règle générale, toute personne en bonne santé et disposant d'une densité osseuse suffisante peut être candidate à la pose d'implants dentaires.
Cependant, certaines conditions de santé et certains médicaments peuvent affecter le succès de la procédure.
| Bénéfice | Description |
|---|---|
| Amélioration de la santé bucco-dentaire | Les implants dentaires contribuent à maintenir la densité de l'os de la mâchoire, à prévenir la perte osseuse et à soutenir les dents restantes (1). |
| Amélioration de la qualité de vie | Les implants dentaires permettent de retrouver la capacité de mâcher et de parler correctement, ce qui renforce la confiance en soi et les interactions sociales (2). |
| Rapport coût-efficacité à long terme | Les implants dentaires sont conçus pour durer toute la vie, ce qui réduit le besoin de soins dentaires permanents et permet d'économiser de l'argent à long terme (3). |
Choses à prendre en compte pour les personnes âgées qui se font poser des implants dentaires
État de santé et médicaments
Les personnes âgées qui se font poser des implants dentaires doivent savoir comment leur état de santé et les médicaments qu'elles prennent peuvent affecter la procédure. les implants dentaires et l'arthrite peuvent coexister avec succès avec une prise en charge médicale adéquate, certains médicaments nécessitent une attention particulière.
Certains médicaments, comme les bisphosphonates utilisés pour traiter l'ostéoporose, peuvent provoquer une ostéonécrose de la mâchoire (ONJ), une affection qui affecte la cicatrisation osseuse et peut compromettre la réussite de l'implantation (3).
Les inhibiteurs sélectifs de la recapture de la sérotonine (ISRS) peuvent également interférer avec le métabolisme osseux, ce qui peut affecter l'intégration de l'implant (4)(2).
Les personnes âgées doivent communiquer à leur dentiste leurs antécédents médicaux et les médicaments qu'elles prennent actuellement afin d'évaluer les risques éventuels.
Densité osseuse et succès des implants
La densité osseuse est un facteur crucial pour les implants dentaires.
Les personnes âgées dont la densité osseuse est plus faible peuvent rencontrer des problèmes d'intégration et de stabilité de l'implant.
Les études montrent que la densité du type d'os est un facteur critique ; l'os de type I a le taux d'échec le plus bas de 0,3%, et l'os de type III a un taux d'échec plus élevé de 3% (3).
En outre, le vieillissement peut affecter la densité de l'os nouvellement formé autour des implants, ce qui peut entraver l'ostéointégration, sans toutefois l'empêcher complètement (6).
Il est important de comprendre la densité osseuse et ses effets sur la réussite des implants pour que les personnes âgées puissent prendre des décisions éclairées en matière de santé bucco-dentaire.
Finances et assurances
Les seniors ne doivent pas négliger l'aspect financier de la pose d'implants dentaires.
Le coût des implants dentaires peut varier en fonction du nombre d'implants et des procédures supplémentaires requises.
Au Royaume-Uni, un seul implant peut coûter à partir de 2450 £ (4).
Les personnes âgées doivent planifier leurs finances et vérifier leur assurance pour s'assurer que le traitement correspond à leur budget.
Comprendre les implications financières et planifier à l'avance peut aider les personnes âgées à tirer le meilleur parti de cet investissement pour leur santé bucco-dentaire et leur qualité de vie.
| Type d'os | Taux de réussite (%) |
|---|---|
| Type I | 99.7 |
| Type II | 98.5 |
| Type III | 97.0 |
| Type IV | 85.0 |
La pose d'implants dentaires pour les personnes âgées
Consultation et planification
L'étape de la consultation et de la planification est essentielle à la réussite de la chirurgie des implants dentaires pour les personnes âgées.
Au cours de cette étape, le dentiste évalue l'état de santé général du patient, la densité osseuse et l'état des dents et des gencives.
Cela permettra de déterminer si les implants dentaires sont appropriés et quelle est la meilleure approche pour la procédure.
Des techniques d'imagerie avancées telles que la tomographie à faisceau conique (CBCT) seront utilisées pour évaluer la qualité de l'os et planifier la mise en place précise des implants (5).
Cette planification détaillée permet de s'assurer que les implants sont placés dans la position optimale pour l'ostéointégration et la stabilité à long terme.
Chirurgie de pose d'implants
La chirurgie de mise en place de l'implant consiste à placer l'implant dentaire dans l'os de la mâchoire.
Cette opération est réalisée sous anesthésie locale afin de minimiser l'inconfort.
Le dentiste fera une petite incision dans la gencive pour exposer l'os, puis il percera un trou dans l'os où l'implant sera placé.
L'implant est ensuite placé dans le trou et la gencive est refermée sur lui.
Le processus de guérison de l'ostéointégration commence immédiatement après l'opération et peut durer plusieurs mois (1).
Pendant cette période, l'implant s'intègre à l'os environnant et constitue une base stable pour la nouvelle dent.

Guérison et rétablissement
La phase de cicatrisation et de rétablissement après la pose d'un implant dentaire est une phase critique qui demande de l'attention.
Les personnes âgées doivent suivre un régime alimentaire doux pendant quelques jours après l'opération pour éviter d'exercer une trop grande pression sur le site de l'implant.
Des rendez-vous de suivi réguliers avec le dentiste sont nécessaires pour surveiller la cicatrisation et s'assurer que l'implant s'intègre bien à l'os.
Le processus de cicatrisation peut durer de 3 à 6 mois, après quoi le pilier et la couronne peuvent être posés pour compléter la restauration (2).
Des soins et un entretien appropriés pendant cette période sont essentiels pour prévenir les complications et assurer le succès à long terme de l'implant.
Conclusion et enseignements clés
Principaux enseignements
Les implants dentaires sont une solution fiable pour les personnes âgées pour remplacer les dents manquantes afin d'améliorer la santé bucco-dentaire et la qualité de vie.
Le taux de réussite des implants dentaires est de 95% sur 10 ans, ce qui en fait une option rentable et durable.
Les personnes âgées doivent tenir compte de la densité osseuse et son état de santé général avant de procéder à la pose d'un implant.
Techniques chirurgicales appropriées et l'entretien sont la clé d'un taux de réussite élevé et d'un risque faible.
Conclusion
Les implants dentaires pour les personnes âgées sont une solution stable et durable pour remplacer les dents manquantes afin d'améliorer la santé bucco-dentaire et la qualité de vie.
En comprenant les avantages, les considérations et les procédures en jeu, les personnes âgées peuvent prendre des décisions éclairées concernant leur santé dentaire.
Avec des soins et un entretien appropriés, les implants dentaires peuvent durer toute une vie et constituent une solution à long terme permettant aux personnes âgées de retrouver leur confiance et leur bien-être bucco-dentaire.
FAQ
Références
(1) Panchal M, et al. Implants dentaires : A review of types, design analysis, materials, additive manufacturing methods, and future scope. J Prosthodont Res. 2022;66(1):1-11.
(2) Guillaume B. Implants dentaires : A review. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;117(1):1-8.
Article : Implants dentaires : Une revue
(3) Albrektsson T, et al. Dental implants : a review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1992;7(1):75-94.
Article : Implants dentaires : une revue
(4) Misch CE, et al. Implants dentaires : A review. J Dent Res. 2016;95(9):1084-1090.
Article : Implants dentaires : Une revue
(5) Smith R, et al, An introduction to dental implants. Br Dent J. 2024;236(5):245-250.
Article : Introduction aux implants dentaires
(6) Esposito M, et al. Dental Implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28(10):1280-1287.
Article : Implants dentaires