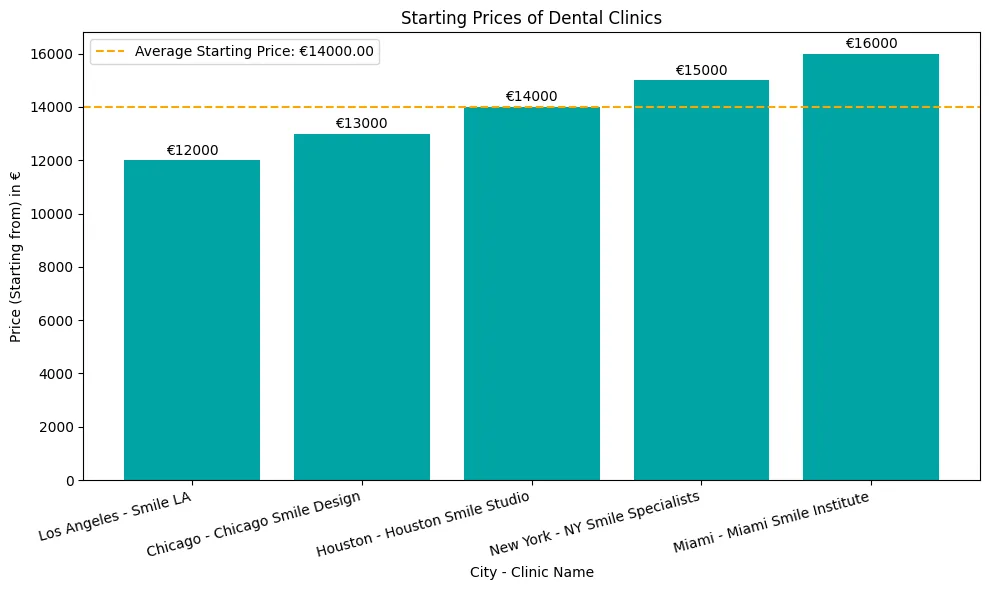
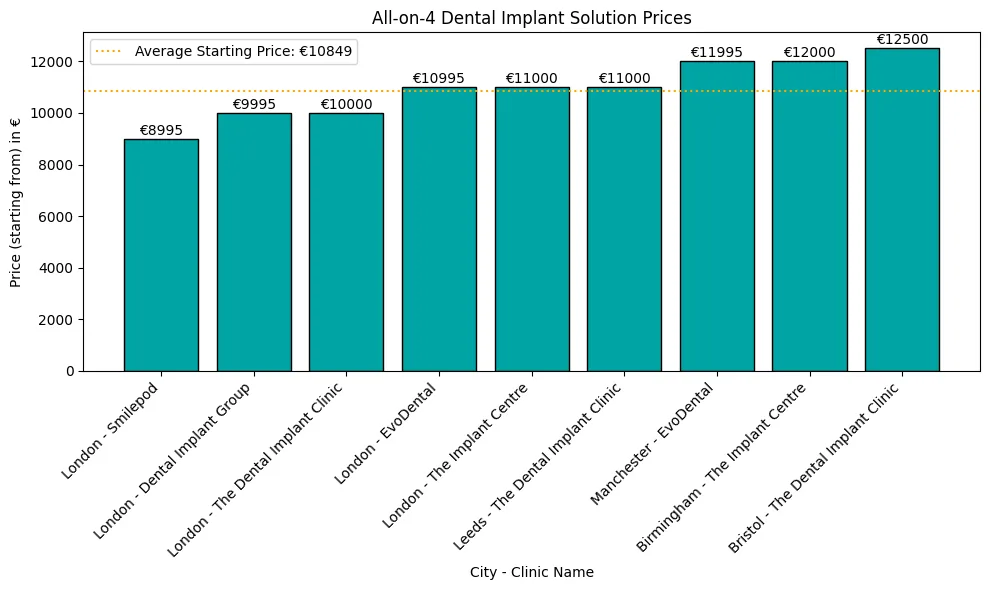
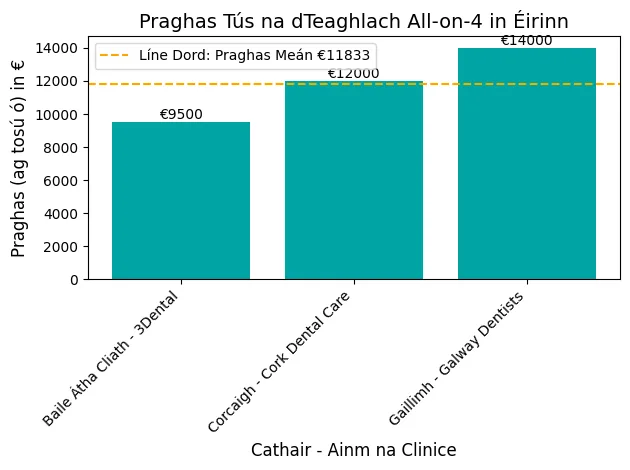
Zahnimplantate können überwältigend sein, wenn es darum geht, fehlende Zähne zu ersetzen. Wenn Sie jedoch über die Unterschiede zwischen den verschiedenen Zahnimplantat-Typen verwirrt sind und nicht wissen, welches das richtige für Sie ist, sind Sie nicht allein.
Welche Arten von Zahnimplantaten gibt es?
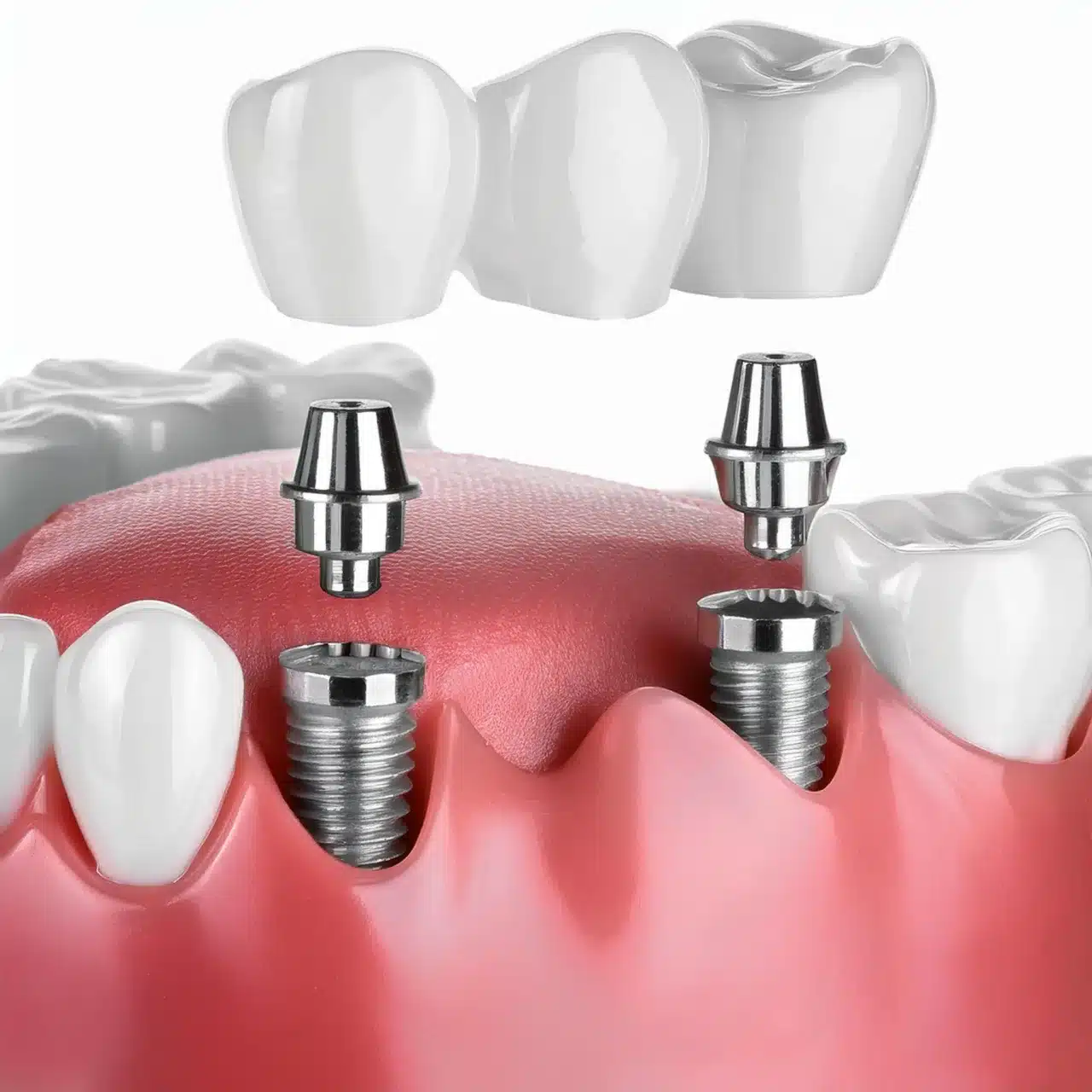
Die Arten von Zahnimplantate sind enossal, subperiostal und zygomatisch. Endosteale Implantate, die häufigsten, werden direkt in den Kieferknochen eingesetzt. Subperiostale Implantate liegen auf dem Knochen unter dem Zahnfleisch auf. Jochbeinimplantate, die bei unzureichendem Kieferknochen verwendet werden, sind im Wangenknochen verankert. Jeder Implantattyp eignet sich für unterschiedliche Patientenbedürfnisse auf der Grundlage spezifischer Zahnverhältnisse.
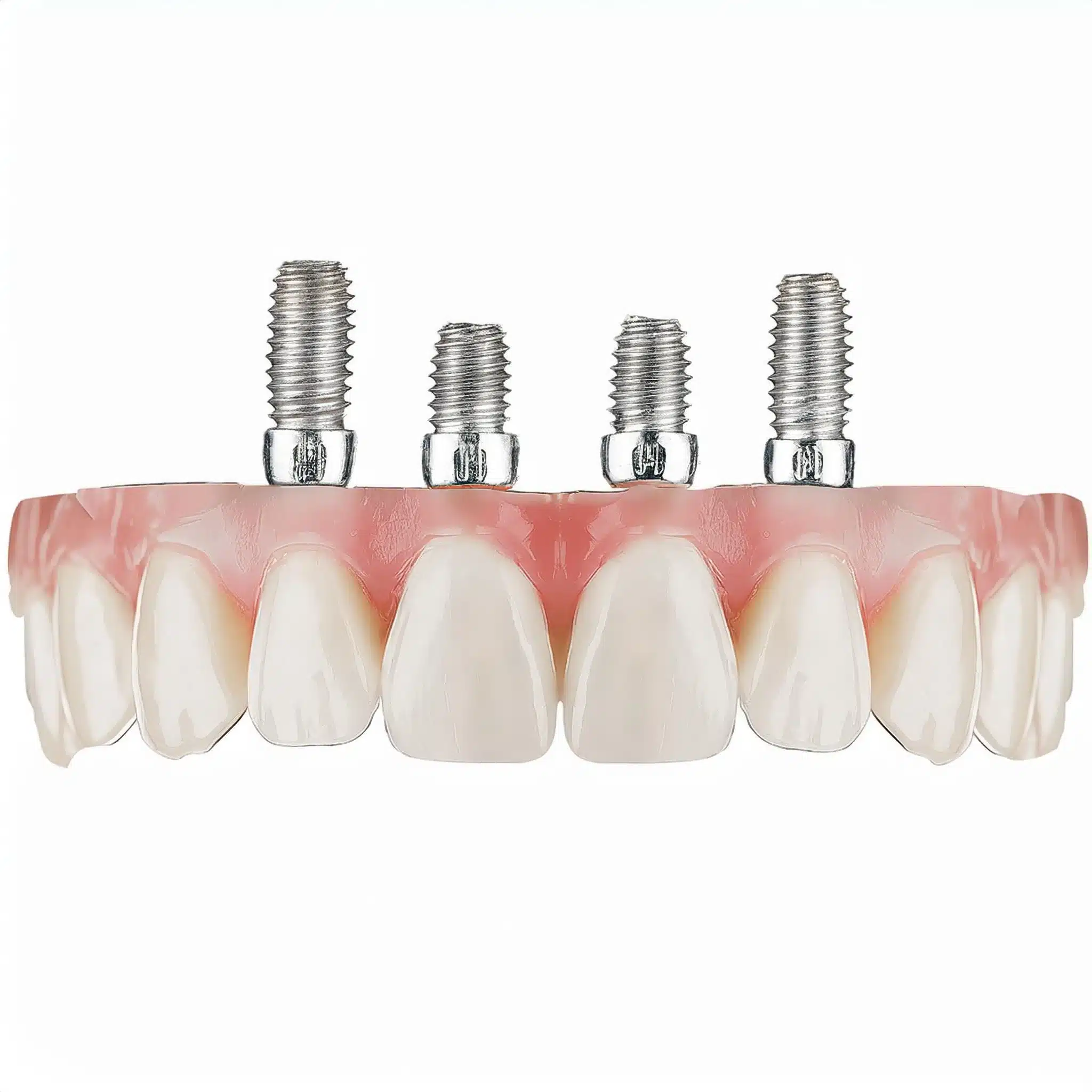
Gestaltung von Zahnimplantaten
Zahnimplantate gibt es in verschiedenen Ausführungen für unterschiedliche Patientenbedürfnisse und Kieferknochenverhältnisse.
Wenn Sie diese Arten kennen, können Sie fundierte Entscheidungen über Ihre zahnärztliche Versorgung treffen.
Endosteale Zahnimplantate
-
Definition: Enossale Implantate sind die häufigsten, schraubenförmig und werden direkt in den Kieferknochen eingesetzt.
Sie werden aus Titan hergestellt und sind für Patienten mit ausreichender Kieferknochendichte geeignet (1).
-
Verfahren: Bohren in den Kieferknochen und Einsetzen des Implantats.
Der Knochen heilt um das Implantat herum ein und fixiert es an seinem Platz.
-
Vorteile: Endosteale Implantate sind für ihre Haltbarkeit und ihr natürliches Gefühl bekannt.
Kann einen Zahn, mehrere Zähne oder einen ganzen Zahnbogen stützen.
Subperiostale Zahnimplantate
-
Definition: Subperiostale Implantate werden unter dem Zahnfleisch, aber auf oder über dem Kieferknochen platziert.
Sie sind für Patienten gedacht, die nicht genügend gesunden natürlichen Kieferknochen haben und sich keinem Knochenaufbau unterziehen können oder wollen (2).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen des Implantats in den Kieferknochen unter dem Zahnfleischgewebe.
Das Zahnfleisch heilt über dem Implantat ein.
-
Vorteile: Subperiostale Implantate für Menschen mit unzureichendem Kieferknochen.
Kann eine stabile Basis für Zahnersatz oder Brücken bieten.
Transosteale Zahnimplantate
-
Definition: Transosteale Implantate werden in bestimmten Fällen eingesetzt, wenn der Kieferknochen zu dünn ist.
Sie werden durch den Kieferknochen und in das Zahnfleischgewebe auf der anderen Seite eingesetzt.
-
Verfahren: Bohrung durch den Kieferknochen, um das Implantat einzusetzen.
Dieser Typ ist weniger verbreitet und wird in besonderen Fällen verwendet.
-
Vorteile: Transosteale Implantate für Patienten mit sehr dünnen Kieferknochen.
Mini-Zahnimplantate
-
Definition: Mini-Zahnimplantate sind kleiner und dünner als Standardimplantate.
Wird zur Stabilisierung von Unterkieferprothesen verwendet (3).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen des Mini-Implantats durch weniger invasive Techniken.
Wird in Fällen verwendet, in denen herkömmliche Implantate nicht möglich sind.
-
Vorteile: Mini-Zahnimplantate sind weniger invasiv und können sofortigen Halt für Zahnersatz bieten.

Arten von Zahnimplantaten bei Knochenverlust
Zahnimplantate können für Menschen mit erheblichem Knochenverlust eine Herausforderung darstellen.
Aber es gibt spezielle Implantate für diesen Fall.
Pterygoid-Zahnimplantate
-
Definition: Pterygoid-Implantate werden bei Knochenverlust im Oberkiefer eingesetzt.
Wird im Kieferknochen hinter dem Oberkiefer platziert (4).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen des Implantats in den Pterygoid-Knochen, der eine stabile Basis für den Zahnersatz bietet.
-
Vorteile: Pterygoid-Implantate für Patienten mit starkem Knochenverlust, um einen stabilen und funktionellen Zahnersatz zu erhalten.
Jochbein-Zahnimplantate
-
Definition: Jochbein-Implantate werden eingesetzt, wenn ein Knochenaufbau nicht möglich ist.
Es wird im Jochbein platziert und reicht bis in den Kieferknochen (2).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen des Implantats in den Jochbeinknochen, der eine stabile Basis für den Zahnersatz bildet.
-
Vorteile: Jochbeinimplantate für Patienten mit unzureichendem Kieferknochen für eine dauerhafte und langlebige Zahnversorgung.

Optionen für Zahnimplantate
Die Wahl des richtigen Verfahrens für Zahnimplantate ist wichtig für ein erfolgreiches Ergebnis.
Es gibt verschiedene Möglichkeiten für unterschiedliche Patienten und Zahnzustände.
Vollmundiges Zahnimplantat
-
Definition: Vollmundige Zahnimplantate bedeutet, ein komplettes Gebiss durch Implantate zu ersetzen.
Dies kann All-on-4 sein, bei dem vier Implantate in den vorhandenen Knochen eingesetzt werden, um einen kompletten Zahnbogen zu tragen (4).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen mehrerer Implantate in den Kieferknochen, die dann einen vollständigen Zahnbogen tragen.
-
Vorteile: Zahnimplantate für den gesamten Mund bei Patienten mit großem Zahnverlust.
Implantat Deckprothesen
-
Definition: Implantat-Überzahnersatz sind implantatgetragene Prothesen, die stabiler sind als herkömmliche Prothesen (1).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen von Implantaten in den Kieferknochen, die dann die Deckprothese tragen.
-
Vorteile: Implantat-Overdentures für eine bessere Kaufunktion und mehr Komfort im Vergleich zu herkömmlichen Prothesen.
Implantatgetragene Brücken
-
Definition: Implantatgetragene Brücken dienen dem Ersatz mehrerer Zähne in einer Reihe. Besteht aus Kronen, die mit Zahnimplantaten verbunden werden (2).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen von Implantaten in den Kieferknochen, die dann die Brücke tragen.
-
Vorteile: Implantatgetragene Brücken für dauerhaften und ästhetisch ansprechenden Mehrzahnersatz.
Sofortige vs. verzögerte Belastung von Zahnimplantaten
Der Zeitpunkt der Belastung von Zahnimplantaten ist wichtig. Wenn Sie den Unterschied zwischen sofortiger und verzögerter Belastung verstehen, können Sie fundierte Entscheidungen für Ihre Zahnpflege treffen.
Verzögerte Belastung Belastung der Implantate
-
Definition: Verzögertes Laden bei Zahnimplantaten bedeutet, dass das Implantat eingesetzt wird und die Einheilung abgewartet wird, bevor ein provisorischer Zahn eingesetzt wird.
Die traditionelle Methode besteht darin, vor der Belastung sicherzustellen, dass das Implantat vollständig mit dem Knochen verwachsen ist (3).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen des Implantats und mehrmonatige Wartezeit, bis der Knochen um das Implantat herum geheilt ist.
Nach der Heilung wird ein provisorischer Zahn eingesetzt.
-
Vorteile: Verzögerte Belastung für ein stabileres und dauerhafteres Ergebnis, da das Implantat Zeit hat, sich vollständig mit dem Knochen zu verbinden.
Sofortige Belastung Belastbare Implantate
-
Definition: Zahnimplantate mit SofortbelastungAuch bekannt als Same-Day-Implantate oder Zähne an einem Tag, bedeutet das Einsetzen eines provisorischen Zahns während desselben Termins wie die Implantation.
Geeignet für Patienten mit ausreichender Kieferknochendichte (4).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen des Implantats und sofortiges Anbringen eines provisorischen Zahns.
Dies kann die gesamte Behandlungszeit verkürzen.
-
Vorteile: Sofortige Belastung für Patienten, um schneller funktionelle und ästhetische Ergebnisse zu erzielen.
Einfacher vs. mehrfacher vs. vollständiger Bogen
Die Wahl der richtigen Zahnimplantatkonfiguration zwischen Einfacher vs. mehrfacher vs. vollständiger Bogen ist wichtig für erfolgreiche und dauerhafte Ergebnisse.
Es stehen verschiedene Optionen zur Verfügung, die jeweils auf die unterschiedlichen Bedürfnisse der Patienten und Zahnverhältnisse abgestimmt sind.
Vollmundige Zahnimplantate
Definition: Zahnimplantate für den ganzen Mund bedeuten, dass ein komplettes Gebiss im Ober- oder Unterkiefer ersetzt wird, z. B. All-on-4, bei dem vier Implantate in den vorhandenen Knochen eingesetzt werden, um einen ganzen Zahnbogen zu tragen (4).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen mehrerer Implantate in den Kieferknochen, die dann einen vollständigen Zahnbogen tragen.
-
Vorteile: Zahnimplantate für den gesamten Mund bei Patienten mit großem Zahnverlust.
Zahnimplantate mit mehreren Zähnen
Definition: Mehrere Zähne Zahnimplantate dienen dazu, mehrere Zähne hintereinander zu ersetzen und bestehen aus Kronen, die mit Zahnimplantaten verbunden werden (2).
-
Verfahren: Einsetzen von Implantaten in den Kieferknochen, die dann die Mehrfachzahnversorgung tragen.
-
Vorteile: Zahnimplantate für dauerhaften und ästhetisch ansprechenden Zahnersatz für mehrere Zähne.

Schlussfolgerung und wichtige Erkenntnisse
-
Wichtigste Erkenntnisse:
-
Es gibt endosteale, subperiostale, transosteale und Mini-Implantate, die jeweils für unterschiedliche Patientenbedürfnisse und Kieferknochenbedingungen geeignet sind.
-
Es ist wichtig, den Unterschied zu verstehen, um eine fundierte zahnmedizinische Versorgung zu gewährleisten.
-
Zahnimplantatverfahren sind Zahnimplantate für den ganzen Mund, Implantat-Overdentures und implantatgetragene Brücken zum Ersatz verschiedener fehlender Zähne.
-
Schlussfolgerung:
Zahnimplantate sind wichtig für Menschen, die fehlende Zähne ersetzen wollen.
Wenn die Patienten die verschiedenen Arten und Verfahren kennen, können sie fundierte Entscheidungen für ihre zahnärztliche Versorgung treffen.
Lassen Sie sich von einem Zahnarzt beraten, um die beste Behandlung für Ihre Bedürfnisse zu finden.

Faq
Referenzen
- Zeitschrift für orale Implantologie
- Referenz: Rutkowski JL. Zeitschrift für orale Implantologie. JOI. 2023;49(3):[Seitenzahlen].
- Artikel: Zeitschrift für orale Implantologie
- Internationale Zeitschrift für Implantologie
- Referenz: Verschiedene Autoren. Internationale Zeitschrift für Implantologie. Int J Implant Dent. 2023;9(1):[Seitenzahlen].
- Artikel: Internationale Zeitschrift für Implantologie
- Zeitschrift für Zahnimplantate
- Referenz: Kulkarni S. Zeitschrift für Zahnimplantate. J Dent Implant. 2023;13(2):[Seitenzahlen].
- Artikel: Zeitschrift für Zahnimplantate
- Zeitschrift für Osseointegration
- Referenz: Verschiedene Autoren. Zeitschrift für Osseointegration. J Osseointegr. 2023;15(2):[Seitenzahlen].
Artikel: Zeitschrift für Osseointegration